Ensuring Excellence and Compliance in the High-Performance Conductor Market
The Vital Role of Certifications in Quality and Safety The high-performance conductor market is a domain where precision, quality, and compliance are not just desired but mandated. In this context, certifications like ISO 9001 and AS 9100, along with specific qualifications like NAVAIR’s Qualified Products List (QPL) status, play a pivotal role. High Performance Conductors: […]

The Advantages of Using Laminated Flexible Busbars in Automotive Design
Laminated flexible busbars are electrical conductors that are designed to provide a compact, flexible, and highly efficient solution for power distribution. They play a critical role in various power applications. Here, we will dive into the various benefits of laminated flexible busbars and explain how they are used in the automotive industry. Click to expand […]

Grounding Strap: An Essential Component for Automotive Safety and Performance
The grounding strap is one of the most important parts of an electrical system. While many people overlook this integral component, it’s crucial for safety and performance in many industries, including automotive. Knowing more about how grounding straps function can help you select the right one for your specific application. Click to expand What Are […]

A Guide to Copper Wires
Copper wires conduct electrical currents that power our homes and electrical appliances we use every day. Copper wire is the preferred conductor for many electrical applications because of the high conductivity of copper, which contributes to its optimal performance. Suitable for a wide range of applications due to its versatility, copper requires less insulation and […]

Types of Copper Alloys
Unlike pure copper, copper alloys are complex formulations of metal with a copper base and alloy elements such as nickel, aluminum, silicon, tin, and zinc in varying concentrations that give the alloy desired properties. Learn more about popular copper alloys and their common applications. ETP and OF Copper Two popular alloys of copper are electrolytic […]
Tags: Copper Alloys
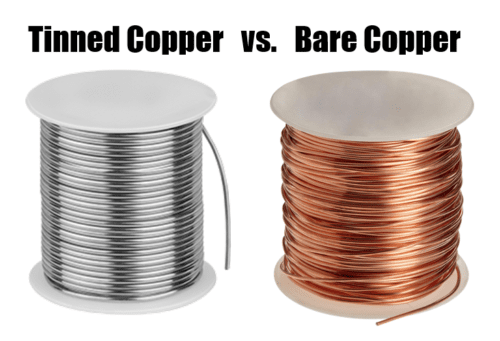
Tinned Copper vs. Bare Copper Wire
Electrical wires and cables made from copper are designed to conduct electric currents. Depending on the application, you may require either bare copper or tinned copper conductors. International Wire Group offers reliable bare and tinned wires and cables that provide top-notch performance in various industries and applications. Learn more about the features, benefits, and applications […]
